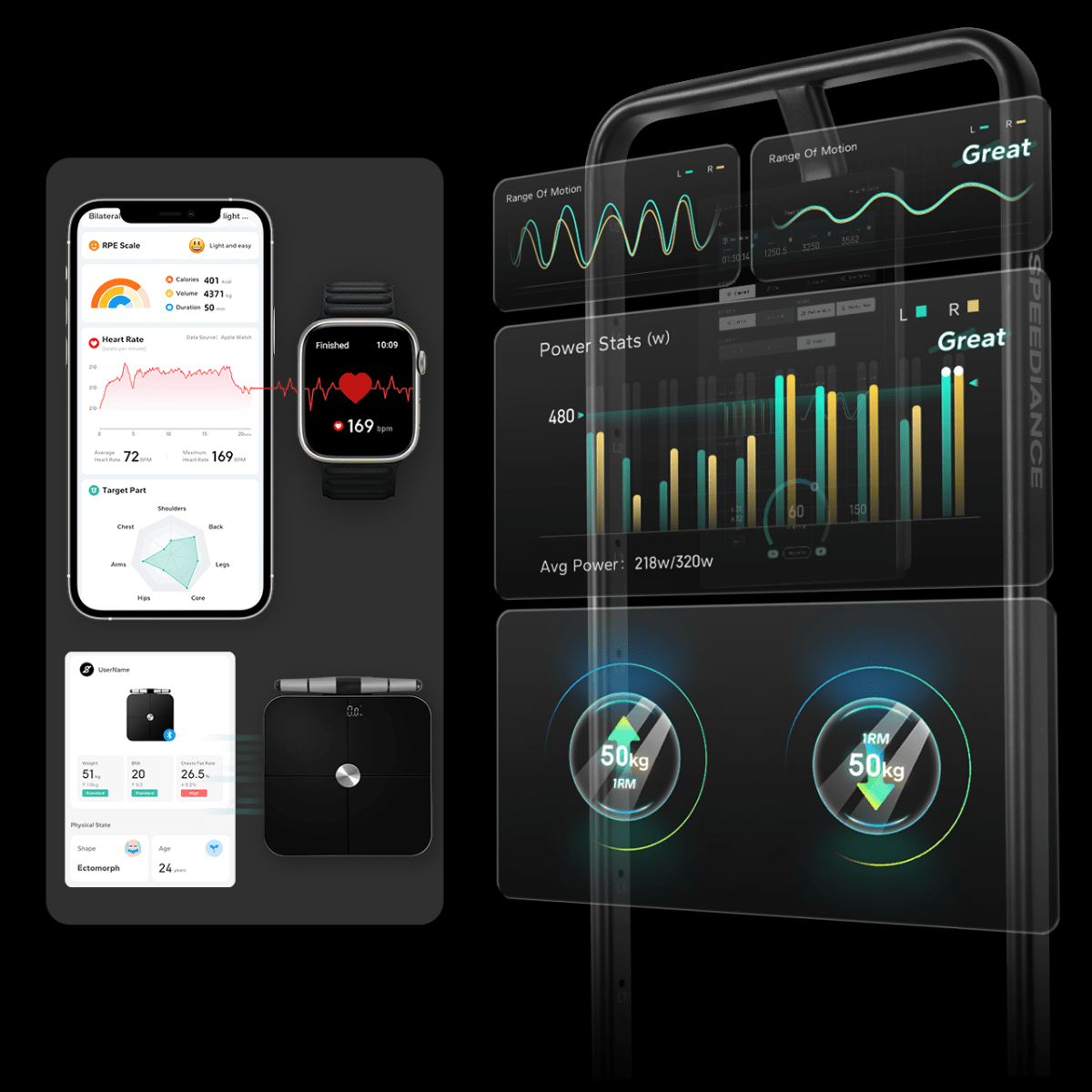
Every time you exercise, your body activates a series of systems to meet increased energy demands. Among these, the respiratory system plays a critical role by supplying oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. Whether you’re running, lifting weights, or practising yoga, your lungs and respiratory muscles are essential for maintaining performance and endurance.
Understanding how your respiratory system adapts to exercise can help you train more effectively and enhance your fitness. By leveraging tools like the Speediance Smart Gym and related fitness solutions, you can optimise your workouts, track progress, and tailor training programs to boost respiratory health and overall performance.
The Respiratory System: Key Components
The respiratory system facilitates oxygen intake and carbon dioxide removal, ensuring that your muscles have the energy they need during physical activity.
Lungs
The lungs are responsible for gas exchange, delivering oxygen to the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide. Exercise increases lung activity to meet the oxygen demands of working muscles.
Airways and Diaphragm
Airways (trachea, bronchi, bronchioles) transport air to the lungs, while the diaphragm, a critical breathing muscle, contracts to allow lung expansion.
Alveoli
These tiny air sacs in the lungs facilitate gas exchange by absorbing oxygen into the blood and expelling carbon dioxide. Exercise improves their efficiency over time, enhancing overall lung performance.
Immediate Responses of the Respiratory System to Exercise
When you begin exercising, your respiratory system quickly adjusts to meet the increased oxygen demand.
Increased Breathing Rate and Tidal Volume
Your brain signals an increase in breathing rate (tachypnoea) and tidal volume (amount of air per breath), ensuring that oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal keep pace with the exercise intensity.
Enhanced Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Exchange
As exercise intensifies, your respiratory and cardiovascular systems collaborate to deliver oxygen efficiently to muscles and expel carbon dioxide.
Long-Term Respiratory Adaptations to Exercise
Regular physical activity leads to significant improvements in the respiratory system’s capacity and efficiency.
Increased Lung Capacity
Consistent exercise enhances lung capacity, enabling your lungs to take in more oxygen per breath and reducing fatigue during prolonged activity.
Improved Gas Exchange Efficiency
The alveoli adapt by increasing their surface area, improving the transfer of oxygen to the blood and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Strengthened Respiratory Muscles
Exercise strengthens the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles, making breathing more efficient and less taxing during high-intensity activities.
Enhanced Oxygen Utilisation
Your body becomes better at extracting and utilising oxygen, improving endurance and allowing you to perform at higher intensities for longer periods.
The Role of Respiratory Fitness in Endurance
For endurance activities like running, cycling, or swimming, respiratory efficiency is crucial. Adaptations in lung capacity, muscle strength, and oxygen utilisation allow athletes to maintain performance and recover faster.
By combining respiratory-focused training with equipment like the Rowing Bench or Adjustable Bench, you can achieve improved respiratory and muscular endurance.
Factors Influencing Respiratory Adaptations
Several factors affect how your respiratory system responds to exercise:
Age
Lung capacity naturally decreases with age, but regular exercise can help mitigate this decline and maintain respiratory health.
Fitness Level
Active individuals typically have more efficient respiratory systems, with greater lung capacity and better oxygen delivery.
Environmental Conditions
High altitudes, poor air quality, or extreme humidity can influence how well your respiratory system functions during exercise.
With the Smart Bluetooth Ring Controller, you can adjust resistance levels and adapt your workouts to your environment, ensuring consistent progress.
Improving Your Respiratory Fitness
To optimise your respiratory system for better performance, consider the following strategies:
Breathing Exercises
Practices like diaphragmatic breathing improve lung capacity and train respiratory muscles for efficiency.
Aerobic Training
Cardio activities like running, swimming, or cycling enhance oxygen delivery and utilisation, boosting respiratory fitness.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT alternates between intense bursts of activity and rest, challenging your respiratory system to adapt and become more efficient.
Customised Workouts with Speediance
The Speediance Smart Gym provides tailored training programs that target respiratory health while incorporating strength and cardio exercises.
Complementary Speediance Solutions
In addition to improving respiratory fitness, Speediance offers tools and accessories to support holistic training:
-
The Weight Lifting Belt helps stabilise your core during strength workouts, reducing the risk of strain while enhancing respiratory performance.
-
The Storage Rack ensures your gym space stays organised, allowing you to focus on efficient workouts.
-
Explore the Accessories Collection for tools that complement your fitness goals, from flexibility to endurance training.
Conclusion
Your respiratory system plays a vital role in exercise performance and overall fitness. By understanding its adaptations to physical activity, you can train smarter and more effectively. Regular aerobic and strength training, paired with tools like the Speediance Smart Gym and its accessories, enables you to optimise respiratory health and reach your goals faster.
Take the first step toward enhanced respiratory fitness today. Contact us for personalised recommendations and discover how Speediance can transform your training routine.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional before starting a new fitness program.
